Memory Allocation Spaces
The eRTOS memory configuration contains multiple allocation spaces (MSpaces). The eRTOS kernel
- Memory allocation requests from RTAPIs, including from C-Runtime libs, are allocated within the external allocation space (ExtMSpace).
- Memory needs from the kernel for internal objects are allocated within the internal allocation space (IntMSpace).
Memory is allocated from one of the process MSpaces unless the memory is required to stay over process exit, such as memory for IPC objects (like events and semaphores) and cross-process shared memory. Such allocations are made from the kernel’s MSpaces.
The diagram below depicts an example of memory allocation for a Process / system process from the HAL Non-paged Pool to external and internal MSpaces.
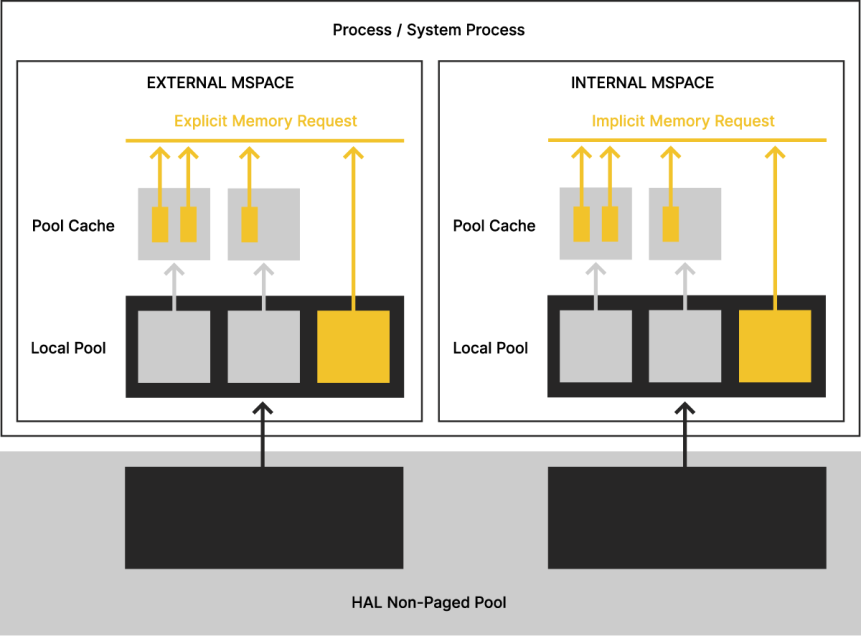
In the HAL Non-paged Pool, black is memory allocated to the Local Pool.
In the Local Pool:
- Black is memory allocated from the HAL Non-paged Pool but freely available to a process.
- Gray is memory allocated from the pool to the Pool Cache used to fulfill small process memory requests.
- Red is large memory requests directly made by the process. Large requests bypass the Pool Cache to improve performance.
- The total pool memory is the sum of used/allocated memory plus free memory.
In the Pool Cache:
- Gray represents the free memory available to the process.
- Red represents memory explicitly allocated by the process.
A number of MSpace default values can be configured in the eRTOS Runtime Configuration file, RtKrnlConfig.ini, or individually through Run.
A process’ MSpaces are allocated on first request for memory. When you start a real-time process using Run, MSpaces are always allocated at process startup before any code in the process executes.
The table below lists the allocation spaces for various types of memory requests:
| Memory requests from... | Local memory |
|---|---|
| C-Runtime libs (new, malloc, realloc, calloc, etc.) | Process ExtMSpace |
| RtAllocateLocalMemory(Ex) | Process ExtMSpace |
| HeapAlloc/HeapReAlloc | Process ExtMSpace |
| VirtualAlloc | Process ExtMSpace |
| RtAllocateLockedMemory | Process ExtMSpace |
| IPC (RtCreateSharedMemory, etc.) | System ExtMSpace |
| RtCreateProcess | Process IntMSpace |
| RtCreateThread | Process IntMSpace |
| RtCreateEvent, RtCreateSemaphore, … | System IntMSpace |
Related Topics:
