|
|
When you use RtssRun to run an RTSS process, it scans the RTSS process service slots for a free slot. If successful, the slot number of the new process is returned as the process ID; otherwise, RtssRun returns -1.
Whenever you rebuild a boot-time RTSS application, you must rerun RtssRun in order to reregister it with the subsystem and access the new version.
NOTE: Environment variables are not automatically expanded.
To run an RTSS application:
Type the following at a command prompt:
RTSSRun [/q /n /l /a
/y
(affinity_mask) /p<ideal_processor>] filename.rtss
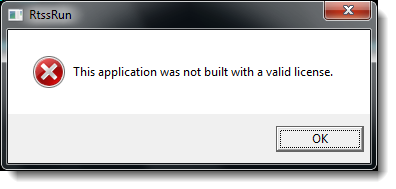
NOTE: If the RTSS application you are trying to run has not be stamped by the StampTool, an error message will appear:

See StampTool for instructions on stamping RTSS applications.
NOTE: Members of the RTXUsers group can run RTSS applications via RtssRun, which starts the RTX Subsystem. However, these members will not be able to see the run status of the subsystem in the RTX Properties control panel, due to the group's access restrictions. For more information, see User Groups and Access Permissions.
The following command runs sample.rtss and displays a message if sample.rtss
fails to load:
RtssRun sample.rtss
The following command runs sample.rtss but does not indicate failure.
RtssRun /q sample.rtss
The following command runs sample.rtss using memory from the RTX local
memory pool.
RtssRun /l sample.rtss
The
following command runs sample.rtss, specifying processors 2 and 3 for the processor affinity
mask.
RtssRun /a(2,3) sample.rtss
The following command runs sample.rtss, specifying processor 2 as the ideal processor.
RtssRun /p2 sample.rtss