Open topic with navigation
Configuring Starvation Behavior
You can make the RTX Scheduler monitor
for highly CPU-intensive RTSS applications and notify the RTX subsystem
if Windows has not been allowed to run for a period of time that you specify.
The timeout value for Windows starvation will depend on RTX load, Windows
application load, and whether or not your application uses multimedia
timers.
You can configure how RTX treats these Windows starvation notifications:
- When notifications are treated as starvation exceptions,
all RTSS applications are stopped or frozen.
- When the notifications are treated as requests
to yield to Windows, the RTX scheduler performs a context switch from
RTSS to Windows for the remaining time of the current HAL timer period, possibly
delaying an RTSS thread for up to one HAL timer period. This could affect
some RTSS applications or drivers if there is a real time interrupt or
timer being serviced at a very high rate (>10 KHz) and this latency
is a significant fraction of the time between events. If this is the case,
increase the starvation timeout value until the expected behavior is achieved.
To
configure starvation settings:
- Open RTX
Properties in Control Panel.
- Click the Starvation
tab.
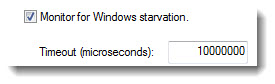
- Select Monitor
for Windows starvation to enable the starvation behavior. By default, this option is disabled.
- Enter the number of microseconds of the starvation
time out period in the Timeout
box. The minimum value is 1 and the maximum is 10,000,000.
- Select an option for handling starvation notifications:
- Click OK.

