Setting the RTSS Boot Configuration
When the RTX64 Runtime is installed, you can assign available processors to Windows or RTX64 through the RTX64 Activation and Configuration utility. The RTX64 Activation utility automatically detects the total number of processors on your system.
NOTE: We recommend that you disable Hyper-Threading. If Hyper-Threading remains enabled, it is recommended that you assign an even number of processors between Windows and RTX64. The Windows logical processor and RTSS logical processor must not share the same physical processor.

|
NOTE: This warning icon indicates that the RTSS boot configuration needs to be reconfigured. |
To set the RTSS boot configuration through the Activation and Configuration dialog:
- Launch the RTX64 Activation and Configuration utility from Start > All Programs > RTX64 4.5 > Activation and Configuration.
- In the Activation and Configuration dialog, click Set the RTSS boot configuration.

NOTE: This option requires the RTX64 Runtime to be installed and licensed.
- Assign processors between Windows and RTX64. For example, on a machine with 8 processors, and a Professional Runtime license at minimum, you can assign up to 7 processors for RTX64.
NOTE: We recommend you do not split Hyper-threaded cores between Windows and RTX64, as it can cause loss of determinism.
- Click Apply to complete configuration.
NOTE: The Apply button remains grayed-out until a valid configuration is provided.
- When you are prompted, click Yes to reboot your computer.
- Restart the system. Choose the RTX64 boot configuration at system startup.
NOTE: If you change the number of Windows processors, you must reboot your system to reallocate processors between Windows and RTSS. If you change the number of RTSS processors after RTX64 was already configured, you only need to restart the RTX64 Subsystem. The Subsystem will continue to work using the old configuration until you restart it.
To set the RTSS boot configuration from the command line:
- Navigate to
%RTX64COMMON%\bin.
- Open a Windows command prompt with Administrator permissions.
- Provide the number of Windows
-wand RTSS-rprocessors. For example, to assign 3 processors to Windows and 5 processors to RTX64, you would type:
Rtx64ActivationUtil.exe -w 3 -r 5
- Restart the system.
NOTE: See RTX64 Activation Usage for a full list of supported command line parameters.
RTSS Processor Validation
RTX64 validates changes to the RTSS boot configuration and warns when pending changes will cause conflicts with existing ideal processor and affinity mask assignments.
Boot Configuration Validation
The validation performs these system checks:
| Validation checks whether... | If validation fails... | To resolve the issue... |
|---|---|---|
|
The Subsystem is fully functional. |
A warning appears from the RTX64 System Tray. |
Reinstall RTX64. |
|
An RTSS boot entry exists. |
A warning appears from the RTX64 System Tray. |
Use the Activation and Configuration utility to create an RTSS boot configuration. |
|
The system is booted into the RTSS boot entry. |
A warning appears from the RTX64 System Tray. |
Boot into the RTSS boot entry. |
Processor Assignment Validation
The validation process checks for conflicts with the RTX64 boot configuration and the Subsystem settings for customer-provided processor assignments. These Subsystem settings are validated:
Ideal processor assignments
|
Affinity mask assignment
|
When a proposed boot change will result in assignment incompatibilities, RTX64 displays a warning with a link to the RTX64 tool through which the issue can be resolved.
Example:
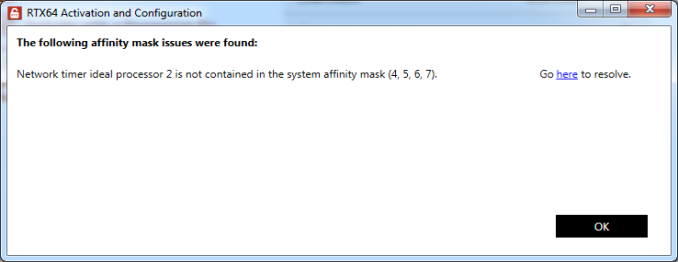
The validation process writes these communications to the RTX64 event log:
- Error messages
- Configuration successful (no errors)
You can access RTX64 event log entries from the Windows Event Viewer under Event Viewer > Windows Logs > Application.
